NONLINEAR WAVES AND VIBRATIONS IN GRANULAR MATERIALS
Damping in granular environments in a few minutes ...
![]()
We focus on the propagation and attenuation of waves and vibrations in granular media, like sand, by conducting experiments on model systems in the laboratory. The particularities of granular media are (i) that they interact according to very nonlinear Hertz potential when they are dry, and more generally (ii) they involve singular mechanisms associated with contacts between geometrically heterogeneous particles : this is the case of wet granular media, particularly colloidal suspensions, when an interstitial fluid is confined between the particles and causes a complex elasto-hydrodynamic interaction.
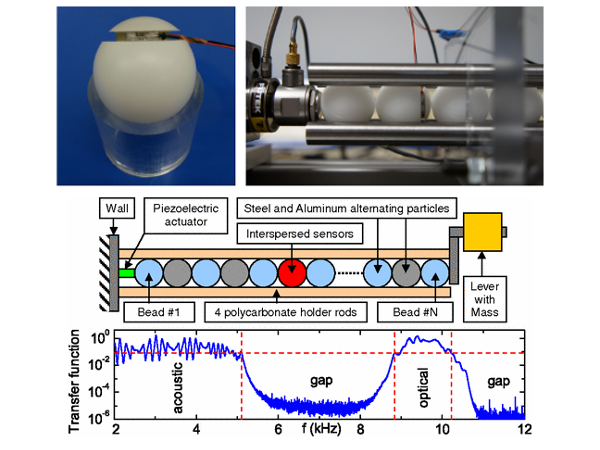
The propagation of waves in a phononic crystal creates an alignment of centimetric particles interacting via Hertz’s nonlinear potential ; an instrumented particle reveals the inaccessible wavelengths of such networks (PRL 2005, PRL 2010).
Another advantage of granular media is that they (iii) present crystalline symmetries when the particles are the same or on the contrary (iv) in disorder when the grains are polydispersed. Lastly, they are known (v) to be highly dissipative, in particular by activating powerful frictional effects.
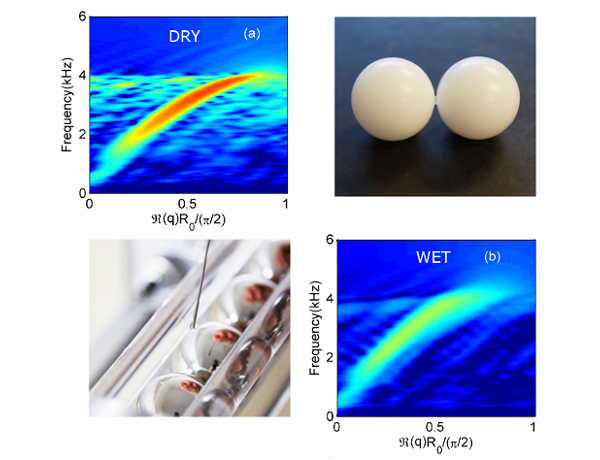
Wave propagation in a granular material wetted by the addition of a small quantity of viscous interstitial fluid ; measuring the relation of dispersion shows that the fluid initiates an elasto-hydrodynamic interaction resulting in the stiffening of contacts, increased propagation speed and greater dissipation (Thèse 2016 Kamil Chrzaszcz)
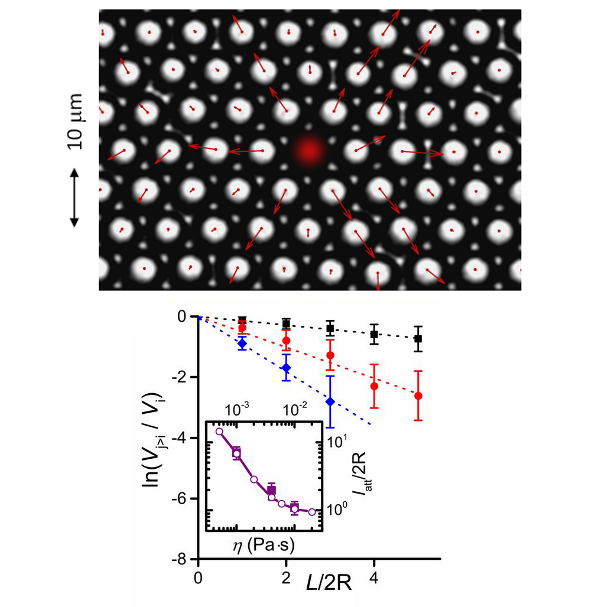
Direct observation of the propagation of a pulse in a colloidal suspension to show the role played by the elasticity of particles, the viscosity of the fluid and the topological disorder in the attenuation length and transport properties (PNAS 2017).
Research carried out in the laboratory, essentially experimental, involves several scales (centimetric, millimetric and micrometric), from contact dynamics (dry and wet), to modelled structures (phononic crystals composed of periodic alignments of spheres), and disordered stacks of vibrated grains (granular dissipator).
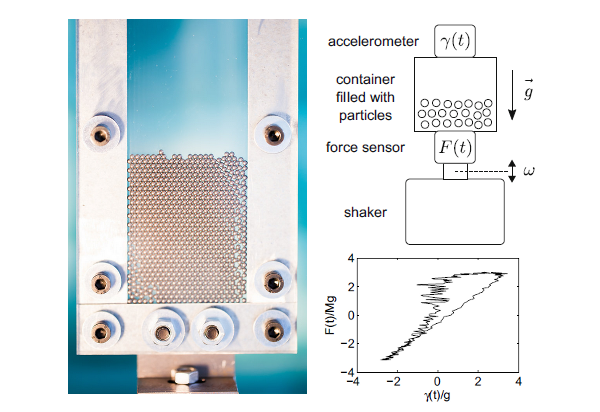
Measure of the loss factor and the effective mass of a granular dissipator ; the loss factor of this system is proportional to the mass of vibrated grains, whose apparent mass decreases until disappearing with the amplitude of acceleration (Thèse 2016 Marwa Masmoudi, Gran. Matt. 2016).
Phase transitions in vibrated granular media. Defense of Rene Zuniga, 25/02/2021



